Do UCs Use AI Detectors? Complete UC System Analysis 2025
Summary
Instead of detection tools, UC campuses emphasize AI literacy, pedagogical redesign, and supported AI tools vetted for privacy. Policies focus on helping students understand responsible AI use rather than policing them with unstable technologies. UC San Diego is the only campus that allows detectors as a non-decisive indicator within a holistic review process.
System-wide, UCOP offers Responsible AI Principles—transparency, privacy, accountability, and equity—without requiring AI detection. Overall, UCs prioritize teaching, process-based assessment, and ethical AI use over automated surveillance.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational and informational purposes only. Students, educators, and researchers should always comply with their institution's academic integrity policies and use AI tools transparently and ethically.
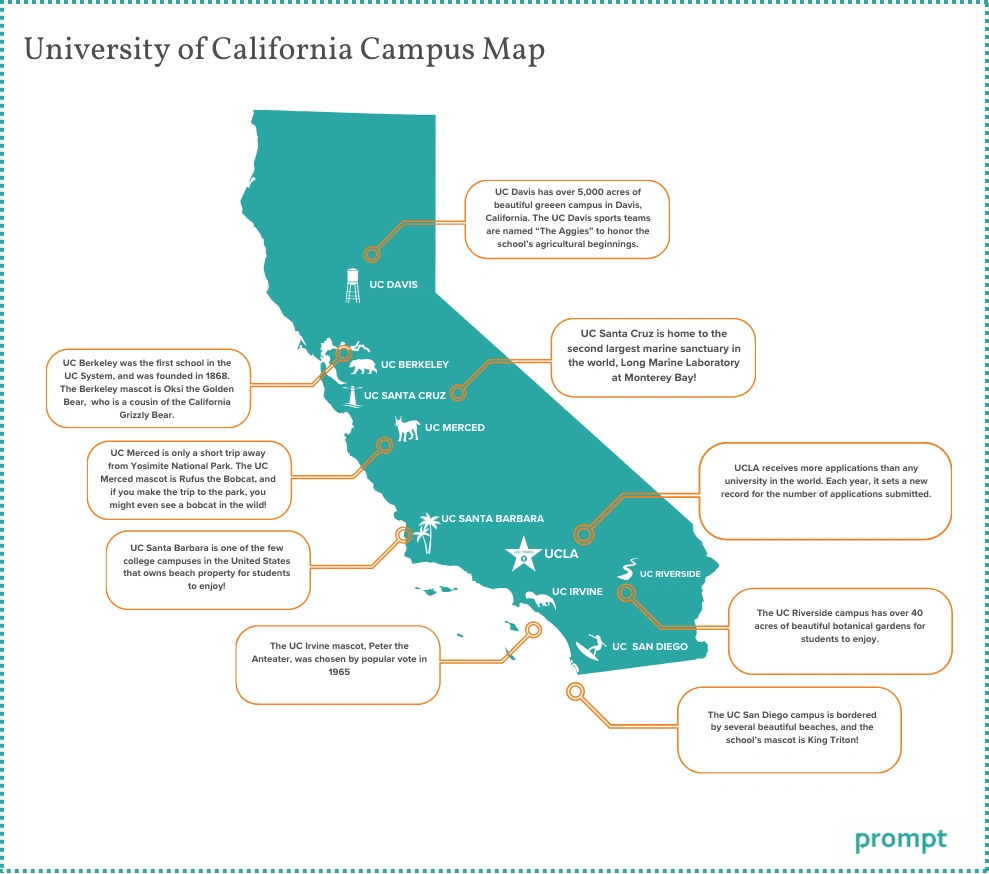
As artificial intelligence tools continue to transform higher education, students and educators are wondering: Do UCs use AI detectors? For a university system with over 280,000 students across 10 campuses, the University of California's approach to AI detection technology has been surprisingly hands-off so far. Here's the comprehensive analysis of AI detector policies in UC universities, a detailed comparison of how different UC campuses approach AI detection, and what these policies mean for the UC academic community.
Important Note: This analysis is intended to help students, faculty, and researchers understand institutional policies. All AI tool usage should comply with your institution's academic integrity requirements.
Summary
In response to the increasing presence of generative AI in higher education, the University of California (UC) system has adopted a measured, educational approach. None of the UC campuses mandate the use of AI writing detectors. Indeed, many of them have formally opted out due to concerns about the reliability, fairness, privacy, and equity of such tools. Rather than relying on detection technologies, UC campuses promote AI literacy, pedagogical innovation, and responsible use of AI tools. This system-wide position demonstrates a commitment to transparency, academic integrity, and the appropriate integration of AI into education while also recognizing the responsibility to educate students on how they can use AI responsibly.
Below is a fully verified breakdown with direct official citations.
UC Campus | AI Detector Policy | Reasons for Not Using AI Detectors |
UC Berkeley | AI detection disabled; Turnitin AI feature not enabled | Accuracy concerns, equity risks, privacy issues, potential for false accusations |
UC Irvine | AI detection not enabled; Turnitin AI tool declined | Lack of transparency, risk of false positives, rapid tech changes, reliability issues |
UC Santa Barbara | AI detectors not recommended | Fallibility of tools, intellectual property risks, misuse as sole evidence |
UCLA | No campus-wide use | Pedagogical focus, ethical use of AI, responsible engagement |
UC San Diego | AI detectors may be reviewed as one indicator only | Unreliable detection, emphasis on holistic evaluation |
UC Riverside | Caution advised | Accuracy and bias concerns, misuse as sole evidence |
UC Merced | No AI detector requirement | Lack of reliable evidence, preference for supported AI tools |
Introduction
As generative AI becomes more prevalent in academic settings, universities face new challenges in maintaining academic integrity. When students wonder "do UC schools use AI detectors" in their work, the answer is nuanced. The University of California (UC) system has made the decision not to require AI writing detectors on its campuses, instead focusing more on educational approaches to use AI. This decision raises interesting questions about how AI should be used in academic processes and the role, if any, detection tools should have. This article provides an overview of the official policies at each UC campus, as well together as the UC system's overall policy and philosophy regarding AI detectors and AI in general in education. This cautious stance highlights the broader challenges and ethics of AI detection in academia that are currently reshaping how universities define academic integrity in the digital age.
Why UC Campuses Are Cautious About AI Detection Tools
The UC system's reluctance to adopt AI detection tools stems from several core concerns:
1. Accuracy Concerns: AI detectors often generate inaccurate or unreliable results. This can lead to false positives, incorrectly flagging student work as AI-generated.
2. Equity Concerns: Multilingual students or students with unique writing styles may be more likely to be flagged by AI detectors, resulting in unfair treatment.
3. Privacy and Data Protection Concerns: Uploading student work to third-party AI systems can raise privacy, FERPA compliance, and intellectual property concerns.
4. Due Process Concerns: UC policies emphasize evidence-based academic integrity approaches, which require objective and reliable evidence. Probabilistic AI scores may not meet these due process standards.
The Current State of AI Detection in UC Universities
1. UC Berkeley
AI Detector Policy: UC Berkeley has explicitly disabled Turnitin's AI writing detection feature, meaning that instructors cannot opt to activate it for their courses.
Reasons for Not Using AI Detectors:
Accuracy Concerns: Berkeley raised concerns about the reliability and accuracy of AI detection tools, particularly in detecting subtle, non-obvious AI-generated text.
Equity Risks: There are concerns that AI detectors could disproportionately flag students who are multilingual or have unique writing styles, potentially resulting in unfair assessments.
Privacy Issues: The university highlighted risks related to privacy, particularly in terms of FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act) compliance, given that uploading student work to third-party AI detection systems could compromise data security.
Potential for False Accusations: A primary concern was the possibility that students might be wrongly accused of academic misconduct based on inaccurate AI detection results.
Alternative Approaches: UC Berkeley focuses on promoting AI literacy and pedagogical transparency. Instructors are encouraged to incorporate AI awareness into their courses, ensuring that students understand the ethical implications of AI use in academic writing.
Official Source: UC Berkeley RTL – Turnitin AI Writing Detection
2. UC Irvine
AI Detector Policy: UC Irvine has formally decided not to activate Turnitin’s AI detection feature for its campus, aligning with the decision of its Integrity in Academics Advisory Committee.
Reasons for Not Using AI Detectors:
Lack of Transparency: One of the key reasons UC Irvine rejected AI detectors was their inability to explain the reasoning behind the detection results. This lack of transparency undermines trust and fairness in the detection process.
Risk of False Positives: There are significant concerns about AI detectors erroneously flagging legitimate student work as AI-generated, leading to potential harm to students' academic records.
Rapid Technological Evolution: The technology behind AI detection tools is rapidly changing, and UC Irvine expressed concerns that the tools would soon become outdated or ineffective.
Reliability Issues: The university’s committee cited the inability of current AI detectors to provide reliable evidence for academic misconduct claims.
Alternative Approaches: Instead of relying on detection tools, UC Irvine emphasizes academic integrity guidelines and encourages responsible AI use. The university also provides resources on how to properly cite AI tools, ensuring that students are equipped to navigate the evolving landscape of AI-assisted writing.
Official Sources: UCI Academic Integrity – AI, Academic Integrity and Citation - Generative AI and Information Literacy - Research Guides at University of California Irvine
3. UC Santa Barbara
AI Detector Policy: UC Santa Barbara’s Writing Program actively advises instructors not to rely on AI detection tools, stating that such tools are often unreliable and pose intellectual property risks.
Reasons for Not Using AI Detectors:
Fallibility of Detection Tools: The UCSB Writing Program points out that AI detectors have a high rate of false positives, making them an unreliable method for identifying AI-generated content.
Intellectual Property Risks: Uploading student work to third-party AI detection systems raises concerns over the security of intellectual property, as student writing could be stored or misused without their consent.
Misuse of Detection as Evidence: The university cautions against using AI detection results as definitive evidence of academic dishonesty, as the tools may fail to accurately identify the authorship of the work.
Alternative Approaches: UC Santa Barbara encourages instructors to focus on creating clear and transparent expectations around AI use in assignments. They promote a pedagogical approach that fosters critical thinking and responsible AI integration, rather than relying on detection tools.
Official Source: UCSB Writing Program – AI Writing Tools
4. UCLA
AI Detector Policy: UCLA does not require or mandate the use of AI writing detection tools across the campus. The focus is on integrating AI responsibly into the educational process.
Reasons for Not Using AI Detectors:
Pedagogical Focus: UCLA emphasizes the importance of fostering a reflective, critical approach to AI, rather than treating AI as a threat to be policed. The university believes that educating students on how to use AI responsibly is more valuable than detecting its use.
Ethical Use of AI: UCLA’s approach focuses on ethical guidelines and academic integrity, allowing students to use AI as a tool for learning while also holding them accountable for proper attribution and transparent practices.
Alternative Approaches: The university provides extensive resources for instructors to help them design assignments that encourage responsible AI use. This includes developing clear policies on AI usage and incorporating AI into assignments in ways that support deeper learning, such as through reflection and critical analysis.
Official Source: Using Generative AI Reflectively and Responsibly in Teaching and Learning - UCLA Teaching & Learning Center
5. UC San Diego
AI Detector Policy: UC San Diego’s Academic Integrity Office (AIO) states that AI detectors may be used as one possible indicator of academic misconduct, but they should not be relied upon as conclusive evidence.
Reasons for Not Using AI Detectors:
Unreliable Detection: UC San Diego acknowledges that AI detection tools can be inaccurate, often leading to misidentifications of AI-generated content.
Holistic Evaluation: The university promotes a more holistic evaluation process, which includes multiple factors such as reviewing drafts, examining version histories, and conducting oral assessments.
Alternative Approaches: UC San Diego emphasizes process-based assessment and encourages instructors to conduct oral or in-person checks as part of the academic integrity process. This allows for a more thorough understanding of students’ work and reduces the reliance on potentially flawed technology.
Official Source: Artificial Intelligence in Education
6. UC Riverside
AI Detector Policy: UC Riverside advises instructors to exercise caution when using AI writing detectors due to their potential accuracy and bias issues.
Reasons for Not Using AI Detectors:
Accuracy and Bias Issues: The university highlights that AI detection tools can be biased, especially when applied to diverse student populations with different writing styles.
Misuse as Sole Evidence: UC Riverside strongly discourages using AI detection as the sole basis for accusations of academic misconduct, given the tool’s fallibility.
Alternative Approaches: UC Riverside encourages instructors to clearly communicate expectations for AI use in their courses and to foster a collaborative, transparent approach to academic integrity.
Official Source: UC Riverside – Academic Integrity for Instructors
7. UC Merced
AI Detector Policy: UC Merced does not require AI writing detection tools, and the university has emphasized its preference for the use of supported AI tools in academic settings.
Reasons for Not Using AI Detectors:
Lack of Reliable Evidence: UC Merced’s policy mirrors that of other campuses in its reluctance to rely on AI detection tools due to concerns about their reliability and accuracy.
Alternative Approaches: The university has compiled a list of approved AI tools such as Microsoft Copilot and Zoom AI, which have been vetted for privacy and security compliance. These tools are promoted as resources for students and faculty to use in academic work, ensuring that their use aligns with the university’s privacy and data governance standards.
Official Source: UC Merced – AI Tools at UC Merced
8. UC System-Wide Perspective
The University of California Office of the President (UCOP) plays a key role in guiding the system’s approach to artificial intelligence and its impact on academic integrity. However, UCOP has not mandated the use of AI detection tools across the system. Instead, the system has emphasized principles of responsible AI use, focusing on transparency, equity, and privacy in academic practices.
● No System-Wide Mandate for AI Detection Tools: UCOP has made it clear that the use of AI writing detection technology is not a requirement at the system-wide level. Each individual campus has the autonomy to determine whether they will use AI detection tools based on their local context and academic needs.
● Responsible AI Principles: UCOP has published a set of Responsible AI Principles to guide the use of AI technologies within the UC system. These principles emphasize:
○ Transparency: Clear communication about how AI tools are used, how data is handled, and how decisions related to AI are made.
○ Privacy: Strong protections for student data and adherence to privacy laws like FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act), ensuring that AI technologies do not compromise students’ personal information.
○ Accountability: Ensuring that the use of AI in education is accountable, with appropriate safeguards in place to prevent misuse or unethical practices.
○ Equity: Prioritizing fairness and inclusivity in the adoption of AI tools, ensuring that AI technologies are accessible and do not disproportionately disadvantage certain groups of students.
● AI as a Tool for Learning, Not Surveillance: By focusing on the educational potential of AI, UCOP encourages campuses to use AI technologies to support teaching, learning, and research, rather than focusing on detection and policing of AI-generated content. This forward-thinking approach reflects a commitment to preparing students to use AI responsibly in their future careers, emphasizing AI literacy and ethical considerations.
● Official Source: UCOP – Responsible Use of Artificial Intelligence
What UC Campuses Are Doing Instead
While many UC campuses have declined to use AI writing detectors, they are not rejecting AI technology altogether. Instead, the UC system is actively developing a forward-thinking approach to AI integration, grounded in AI literacy, pedagogical innovation, and privacy-conscious technology adoption.
● AI Literacy: UC campuses are providing instruction on how the various AI tools function, their limits, and when it is appropriate for students and faculty use them. For example, UCLA, which also has no AI detectors, describes AI as "an instrument that we all engage with" and provides teachers resources on how to create clear AI policies in their courses. Using Generative AI Reflectively and Responsibly in Teaching and Learning - UCLA Teaching & Learning Center.
● Pedagogical Innovation: UC campuses are redesigning tests to assess process rather than a final product that could be produced through AI. For example, UC San Diego promotes assignments that prioritize iterative drafting, reflective writing, and oral articulation (of work that only a student can do): AI can’t easily mimic these skills. Artificial Intelligence in Education.
● Supported AI Tools: UC Merced, as well as other UC campuses, has a list of AI tools that have been approved (including Microsoft Copilot and Zoom AI) and are therefore compliant with privacy and data protection standards. Find UC Merced's AI tool guidelines here.
Taken together, the UC response to AI is neither defensive nor punitive. The lack of AI detectors is simply not an oversight but a conscious decision that reflects values shared across all UC campuses: How students learn to use AI responsibly is more important than trying to catch them with unreliable detection technology.
Conclusion: What AI Checker Does UC Use?
So, do UC schools use AI detectors? Ultimately, no. The stance of the University of California on the use of AI writing detectors is more than just a stance on the use of a particular technology. When students ask "do UCs check for AI?" they should be told that the majority of UCs have decided against them. But UCs have opted for a more holistic approach to AI technology integration that is based on AI literacy, pedagogy, and privacy. In other words, UCs are setting an example in higher education for how AI should be used responsibly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Are AI indicators in Turnitin required by UC?
No. UC decisions in this area are made at the campus level. Some campuses have chosen not to use Turnitin’s AI indicator.
Q2: Which UC campuses have publicly said they’re not using the AI indicator?
As of this writing, UC Berkeley is not using the AI indicator (“opt-out”); UCLA opted out at launch; and UCSD Extended Studies deactivated in 2025. Given the potential for changing policies, always check your local site for the latest information.
Q3: If the AI indicator is enabled for your unit, how should instructors use it?
As one input in a holistic scoring process which could include evaluation of drafts, version history (if available), and conversation/oral checks—especially for low or borderline scores.
Q4. What is the meaning of an asterisk *% in Turnitin?
It means a low (1–19%) AI signal; Turnitin opts not to display a numeric percent at very low values due to the risk of false positives.
Q5. Why do some of our units choose to turn this feature off?
Some units have concerns about reliability, process fairness, privacy or cost. Divisions may use Turnitin for similarity checking only while turning off the AI module.
Q6: What are authoritative AI detection tools available on the market?
Common AI detection tools include Turnitin AI Writing Detection, GPTZero, Originality.AI, GPTHumanizer AI, and Winston AI, though all have reliability limitations as discussed in this article.
Q7: With different campuses having different rules, do UC schools use AI detectors for every single assignment?
No, there is no system-wide requirement for all assignments. Many campuses have moved away from automated policing, choosing instead to focus on AI literacy and critical thinking.
Q8: If a professor decides to verify a student's work, what AI checker does UC use most frequently?
Historically, Turnitin has been the primary tool for similarity reports across the UC system. However, for AI-specific detection, many campuses (like UC Berkeley and UC Irvine) have intentionally disabled Turnitin's AI writing feature. In cases where checking is necessary, they often rely on manual reviews or a combination of indicators rather than a single third-party checker.
Related Articles

Why Formulaic Academic Writing Triggers AI Detectors: A Stylistic Analysis
Why does your original essay look like AI? We analyze how IMRaD structures and low entropy in academ...
Turnitin’s AI Writing Indicator Explained: What Students and Educators Need to Know in 2026
Confused by your similarity score? We explain how Turnitin’s AI writing indicator actually works in ...

Student Data Privacy: What Happens to Your Papers After AI Screening?
Wondering where your essay goes after you hit submit? We uncover how AI detectors store student data...

AI Detection in Computer Science: Challenges in Distinguishing Generated vs. Human Code
AI Detection in Computer Science is unreliable for code: deterministic syntax and tooling cause fals...
